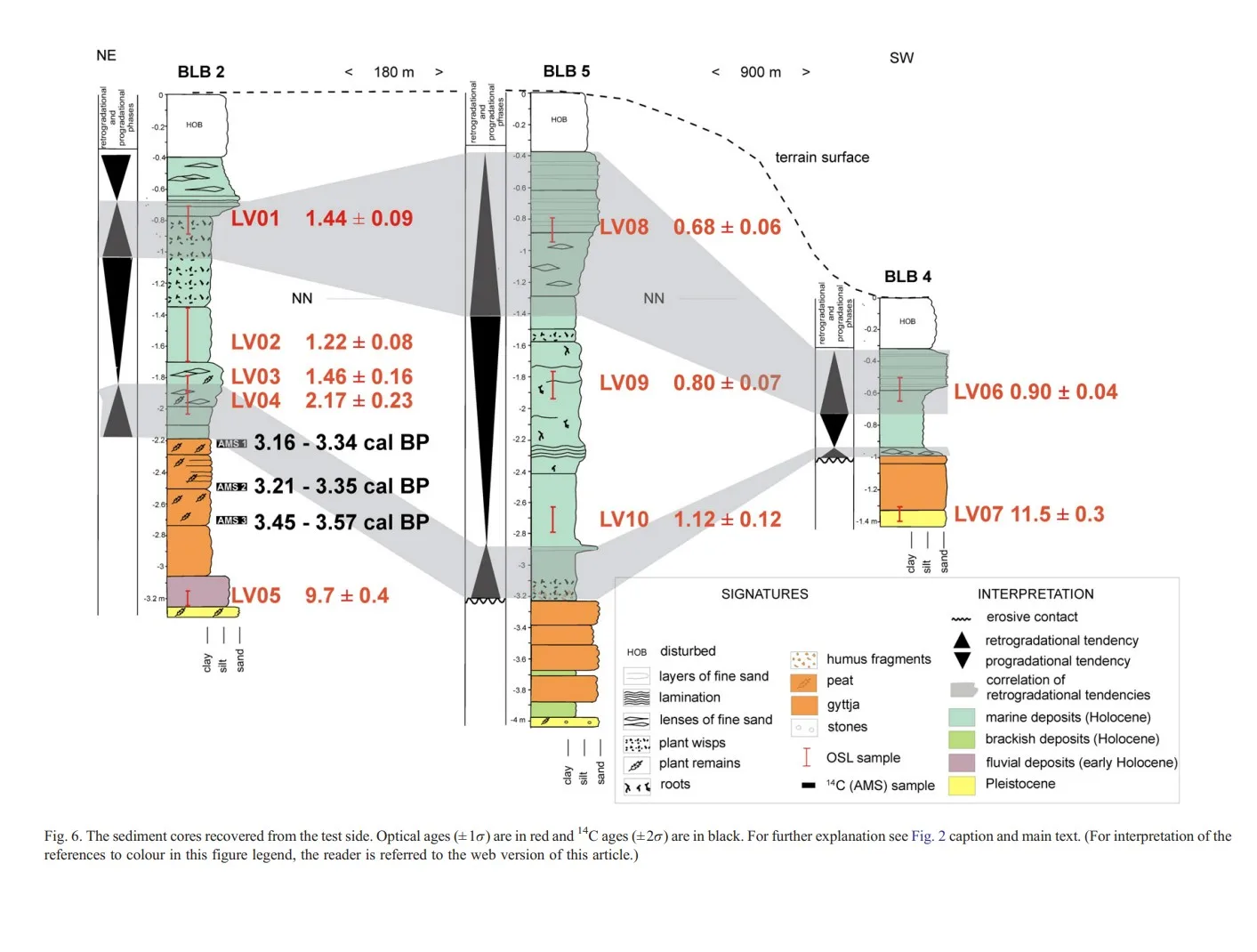
How to reconstruct trends of late Holocene relative sea level: A new approach using tidal flat clastic sediments and optical dating
DOI https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2006.12.001 Abstract Assessment of ongoing relative sea level rise in NW-Europe for individual tidal basins is wanted and, consequently, a variety of methods must be available for investigations under different local conditions. The methodology presented in this paper is based on OSL (optically stimulated luminescence) dating of tidal flat sedimentary records. It uses a conceptual model that assumes that tidal flat clastic sediments record small changes in sea level trend. These changes are in NW-Europe superimposed on the general rising trend of the near-field sea level during the late Holocene (last ∼3500 years). The dating approach can be complemented by 210Pb-dating for the most recent period (last ∼100 years). This combination has the potential to bridge between contrasting short-term and long-term data about sea level change.The paper describes the model for sedimentation and the dating technique. The accuracy of the method is assessed at a test site on the … WeiterlesenHow to reconstruct trends of late Holocene relative sea level: A new approach using tidal flat clastic sediments and optical dating